Attack Transferability Assessment of BERT-ATTACK
Current approaches to attacking large language models rely on the attacker having access to the target model’s parameters, a scenario which is increasingly unrealistic as LLMs are increasingly closed-source. As these powerful models continue to attain wide-spread adoption, there is increasing interest in verifying their robustness to prevent user harm. We observe that many of the current state-of-the-art LLMs derive their architecture from a single common ancestor, BERT. We hypothesize that, if an attacker has knowledge of the data distribution for the downstream task, they can attack one of these BERT-derivative models by using an inexpensive fine-tuned instance of BERT as a surrogate model, and apply existing white-box adversarial attack frameworks to an obfuscated target model.
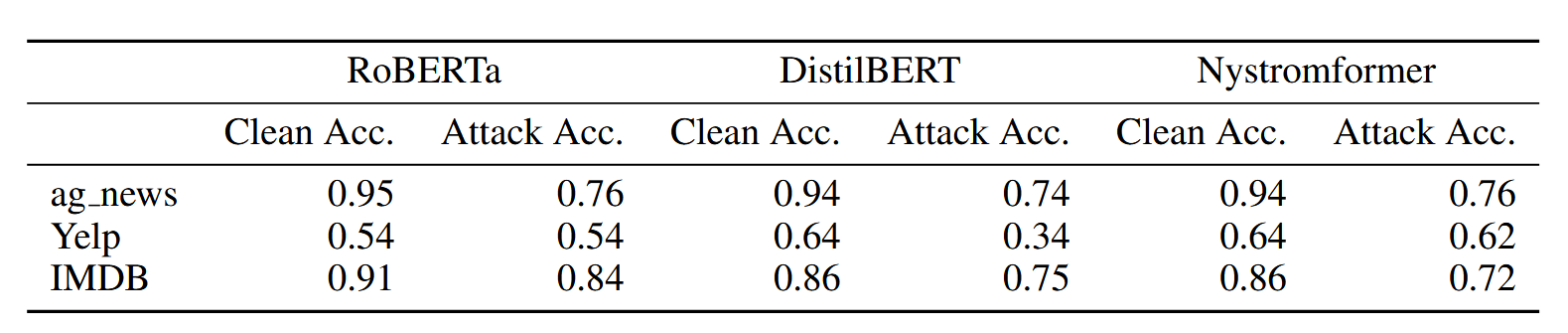
We show merit in the concept of BERT surrogates for black-box attacks against encoder-based LLMs in the case of text classification tasks. On average, we observe a 17% degradation in classifier accuracy in a black-box attack against a variety of BERT-derived architectures using adversarial examples crafted using BERT-ATTACK.
You can find the source code for our model and experiments here, and a more in-depth writeup here
